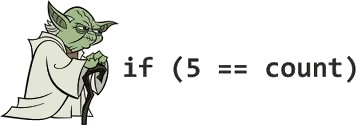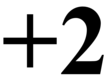Source: http://blog.codinghorror.com/new-programming-jargon/
1. Yoda Conditions
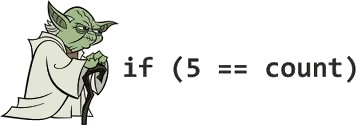
Using if(constant == variable) instead of if(variable == constant), like if(4 == foo). Because it’s like saying “if blue is the sky” or “if tall is the man”.
2. Pokémon Exception Handling

For when you just Gotta Catch ‘Em All.
try {
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Gotcha!
}
3. Egyptian Brackets
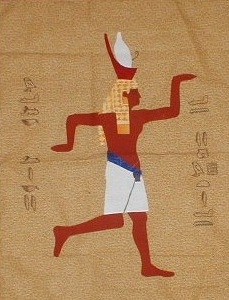
You know the style of brackets where the opening brace goes on the end of the current line, e.g. this?
if (a == b) {
printf("hello");
}
We used to refer to this style of brackets as “Egyptian brackets”. Why? Compare the position of the brackets with the hands in the picture. (This style of brackets is used in Kernighan and Ritchie’s book , so it’s known by many as K&R style.)
4. Smug Report
A bug submitted by a user who thinks he knows a lot more about the system’s design than he really does. Filled with irrelevant technical details and one or more suggestions (always wrong) about what he thinks is causing the problem and how we should fix it.
Also related to Drug Report (a report so utterly incomprehensible that whoever submitted it must have been smoking crack.), Chug Report (where the submitter is thought to have had one too many), and Shrug Report (a bug report with no error message or repro steps and only a vague description of the problem. Usually contains the phrase “doesn’t work.”)
5. A Duck
A feature added for no other reason than to draw management attention and be removed, thus avoiding unnecessary changes in other aspects of the product.
I don’t know if I actually invented this term or not, but I am certainly not the originator of the story that spawned it.
This started as a piece of Interplay corporate lore. It was well known that producers (a game industry position, roughly equivalent to PMs) had to make a change to everything that was done. The assumption was that subconsciously they felt that if they didn’t, they weren’t adding value.
The artist working on the queen animations for Battle Chess was aware of this tendency, and came up with an innovative solution. He did the animations for the queen the way that he felt would be best, with one addition: he gave the queen a pet duck. He animated this duck through all of the queen’s animations, had it flapping around the corners. He also took great care to make sure that it never overlapped the “actual” animation.
Eventually, it came time for the producer to review the animation set for the queen. The producer sat down and watched all of the animations. When they were done, he turned to the artist and said, “that looks great. Just one thing – get rid of the duck.”
6. Refuctoring

The process of taking a well-designed piece of code and, through a series of small, reversible changes, making it completely unmaintainable by anyone except yourself.
7. Stringly Typed

A riff on strongly typed. Used to describe an implementation that needlessly relies on strings when programmer & refactor friendly options are available.
For example:
- Method parameters that take strings when other more appropriate types should be used.
- On the occasion that a string is required in a method call (e.g. network service), the string is then passed and used throughout the rest of the call graph without first converting it to a more suitable internal representation (e.g. parse it and create an enum, then you have strong typing throughout the rest of your codebase).
- Message passing without using typed messages etc.
Excessively stringly typed code is usually a pain to understand and detonates at runtime with errors that the compiler would normally find.
8. Heisenbug
unknown
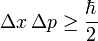
A computer bug that disappears or alters its characteristics when an attempt is made to study it. (Wikipedia)
9. Doctype Decoration

When web designers add a doctype declaration but don’t bother to write valid markup.
10. Jimmy

A generalized name for the clueless/new developer.
Found as we were developing a framework component that required minimal knowledge of how it worked for the other developers. We would always phrase our questions as: “What if Jimmy forgets to update the attribute?”
This led to the term: “Jimmy-proof” when referring to well designed framework code.
11. Higgs-Bugson

A hypothetical bug predicted to exist based on a small number of possibly related event log entries and vague anecdotal reports from users, but it is difficult (if not impossible) to reproduce on a dev machine because you don’t really know if it’s there, and if it is there what is causing it. (see Higgs-Boson)
12. Nopping

I’m writing a scifi novel from the POV of an AI, and their internal language has a lot of programming jargon in it. One of the more generalizable terms is “nopping”, which comes from assembler NOP for no-operation. It’s similar to ‘nap’, but doesn’t imply sleep, just zoning out. “Stanislav sat watching the screensaver and nopped for a while.”
13. Unicorny

An adjective to describe a feature that’s so early in the planning stages that it might as well be imaginary. We cribbed this one from Yehuda Katz, who used it in his closing keynote at last year’s Windy City Rails to describe some of Rails’ upcoming features.
14. Baklava Code

Code with too many layers.
Baklava is a delicious pastry made with many paper-thin layers of phyllo dough. While thin layers are fine for a pastry, thin software layers don’t add much value, especially when you have many such layers piled on each other. Each layer has to be pushed onto your mental stack as you dive into the code. Furthermore, the layers of phyllo dough are permeable, allowing the honey to soak through. But software abstractions are best when they don’t leak. When you pile layer on top of layer in software, the layers are bound to leak.
15. Hindenbug

A catastrophic data destroying bug. “Oh the humanity!”
Also related to Counterbug (a bug you present when presented with a bug caused by the person presenting the bug) and Bloombug (a bug that accidentally generates money).
16. Fear Driven Development

When project management adds more pressure (fires someone, moves deadlines forward, subtracts resources from the project, etc).
17. Hydra Code

Code that cannot be fixed. Like the Hydra of legend, every new fix introduces two new bugs. It should be rewritten.
18. Common Law Feature
anonymous

A bug in the application that has existed so long that it is now part of the expected functionality, and user support is required to actually fix it.
19. Loch Ness Monster Bug

I’ve started Loch Ness Monster bug for anything not reproducible / only sighted by one person. I’m hearing a lot of people in the office say it now. (Possible alternates: Bugfoot, Nessiebug.)
20. Ninja Comments
Also known as invisible comments, secret comments, or no comments.
21. Smurf Naming Convention

When almost every class has the same prefix. IE, when a user clicks on the button, a SmurfAccountView passes a SmurfAccountDTO to the SmurfAccountController. The SmurfIDis used to fetch a SmurfOrderHistory which is passed to the SmurfHistoryMatch before forwarding to either SmurfHistoryReviewView or SmurfHistoryReportingView. If a SmurfErrorEvent occurs it is logged by SmurfErrorLogger to ${app}/smurf/log/smurf/smurflog.log
22. Protoduction

A prototype that ends up in production. Heard this from a tech at the Fermi lab. He said he didn’t coin the term but had heard it used a number of times at Fermi.
23. Rubber Ducking

Sometimes, you just have to talk a problem out. I used to go to my boss and talk about something and he’d listen and then I’d just answer my own question and walk out without him saying a thing. I read about someone that put a rubber duck on their monitor so they could talk to it, so rubberducking is talking your way through a problem.
24. Banana Banana Banana

Placeholder text indicating that documentation is in progress or yet to be completed. Mostly used because FxCop complains when a public function lacks documentation.
///
/// banana banana banana
///
public CustomerValidationResponse Validate()
Other food-related jargon: Programmer Fuel (Mountain Dew, coffee, Mate, anything which gets you well-caffeinated), Hot Potato (Http and Https respectively. Same number of syllables, but more fun to say), Cake (Marty’s noob cake broke the build), Chunky Salsa (based on the chunky salsa rule, a single critical error or bug that renders an entire system unusable, especially in a production environment).
25. Bicrement
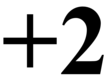
Adding 2 to a variable.
26. Reality 101 Failure

The program (or more likely feature of a program) does exactly what was asked for but when it’s deployed it turns out that the problem was misunderstood and it’s basically useless.
27. Mad Girlfriend Bug

When you see something strange happening, but the software is telling you everything is fine.
28. Megamoth

Stands for MEGA MOnolithic meTHod. Often contained inside a God Object, and usually stretches over two screens in height. Megamoths of greater size than 2k LOC have been sighted. Beware of the MEGAMOTH!
29. Hooker Code

Code that is problematic and causes application instability (application “goes down” often). “Did the site go down again? Yeah, Jim must still have some hooker code in there.”
30. Jenga Code

When the whole thing collapses after you alter a block of code.
This is just the top 30, what I consider to be the most likely candidates for actual new programming jargon based on community upvotes, not just “funny thing that another programmer typed on a webpage and I felt compelled to upvote for hilarity”. Because that would be Reddit. If you’re itching to see even more, there are plenty more answers to read – three hundred and fifty six more to be precise. Longtime Stack Overflow user Greg Hewgill maintains , but this one hasn’t quite made it in there yet. In the meantime, try Stack Printer, or if you have the requisite 10k rep on Stack Overflow, you can view the full soft-deleted question on the site.