Objective : Setup a form with file upload field
Environment
- Spring MVC 3.2.3.RELEASE
- Commons Fileupload 1.3
First let’s code the JSP view of the form. Note below enctype=”multipart/form-data” setting is important, it tells the browser to post the form data as multipart.
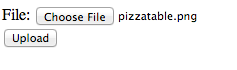
Above JSP will result in a simple file upload form like this:
Then add commons-fileupload 1.3 maven dependency to your pom.xml:
commons-fileupload commons-fileupload 1.3
And configure CommonsMultipartResolver on your spring context. The bean id name is important. Also below I configured it to have maximum file size of 1 mb (1000000 bytes)
Now we’re ready to code the controller handler method. The uploaded file is automatically bound into a object from which you can obtain input stream.
(value = "/", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String upload(("myfile") MultipartFile myFile) {
logger.info("Received file of size " + myFile.getSize() + " bytes");
InputStream inputStream = myFile.getInputStream();
// .. do something with inputStream
inputStream.close();
return "home";
}